Table of Contents
Introduction to Time Travel
Snowflake Time Travel functionality facilitates access to historical data, including data that has been altered or deleted, throughout a defined timeframe. It proves invaluable for various tasks:
- Recovering data-related objects (such as tables, schemas, and databases) that may have been deleted inadvertently or intentionally.
- Creating duplicates and backups of data from specific points in the past.
- Analyzing data usage and manipulation trends over specified time intervals.
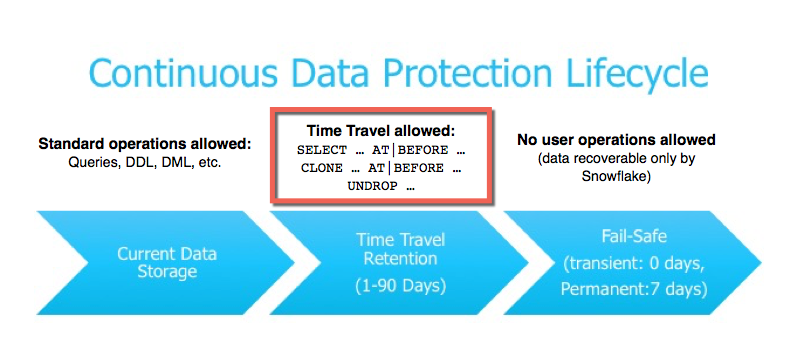
Time travel is part of Continuous Data Protection Lifecycle.
Time Travel SQL Extensions
To facilitate Time Travel, Snowflake has introduced the following SQL extensions:
- The AT | BEFORE clause, which can be utilized in SELECT statements and CREATE … CLONE commands, positioned immediately after the object name. This clause employs one of the following parameters to specify the precise historical data you intend to access:
- TIMESTAMP
- OFFSET (time difference in seconds from the current time)
- STATEMENT (identifier for the statement, such as query ID)
- The UNDROP command, applicable to tables, schemas, and databases, aids in restoring accidentally or intentionally deleted objects.
Data Retention Period
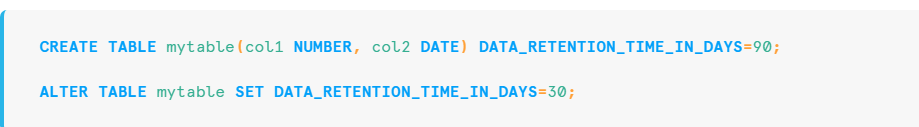
Snowflake preserves the state of data within an object when any DML operation is performed. Since micro partitions are immutable, they come handy for this preserving the state of data. Every object has a data retention period associated with it.
| Object Type | Data Retention Period | Fail Safe | Edition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Permanent Table | 0 to 90 days | 7 days | Enterprise |
| Temporary Table | 0 or 1 (Default 1) | 0 days | Enterprise |
| Transient Table | 0 or 1 (Default 1) | 0 days | Enterprise |
| Tables in Standard editions | 0 or 1 (Default 1) | 0 days | Standard |
Fail Safe
As shown in the above image, after the data retention period is over, the object is moved to fail safe period which is 7 days and non configurable.
With Fail Safe, Only Snowflake support can recover the object and data. Data is not accessible to any other user meaning you are not allowed to query data from fail safe objects.
Fail-safe is a data recovery service
Example:
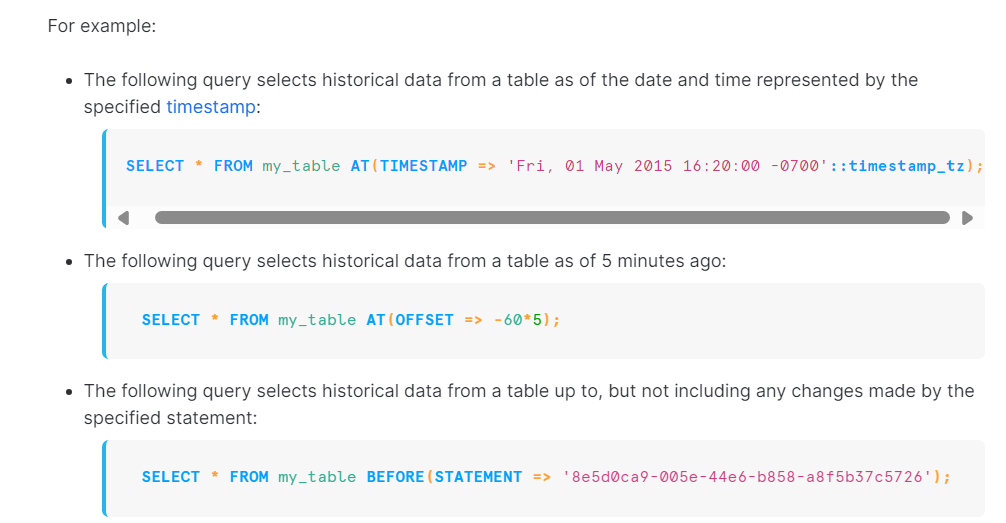
Example of Querying Historical Data
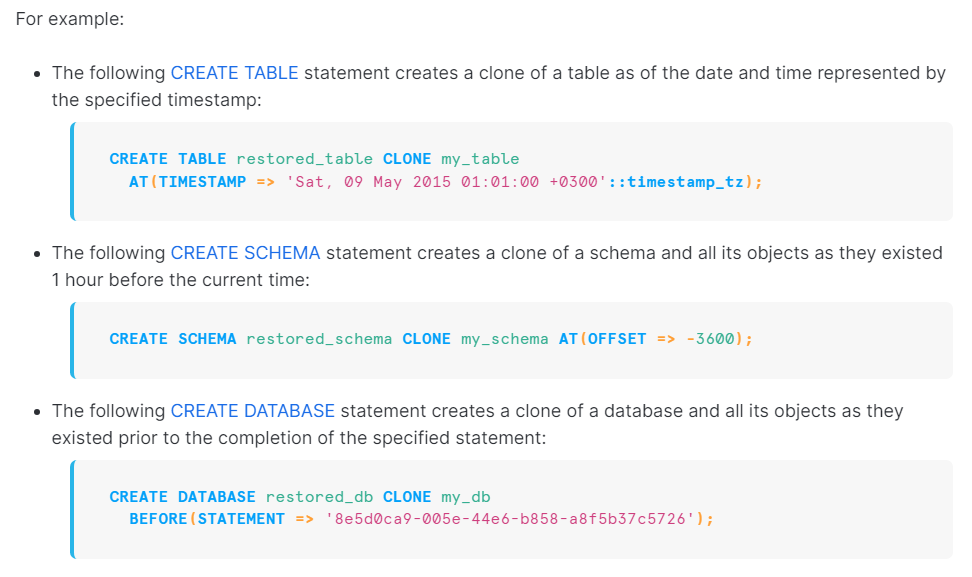
Cloning Historical Objects
Since we can use time travel to access historical data, we can even copy and create the clone of the objects using above SQL extensions. Look at the below examples(Ref Snoflake website) and remember the syntax.
Drop Vs Undrop
When an database object is dropped, it is not removed from Snowflake. It is only marked as Dropped and moves to data retention phase. We can recover or undrop the database object when it is in data retention period. After that, Once it moves to fail Safe State, we can not recover it.
To List dropped objects use HISTORY keyword in show command like below.

To Undrop an object, use the commands like below:

More information please visit Understanding & Using Time Travel | Snowflake Documentation



